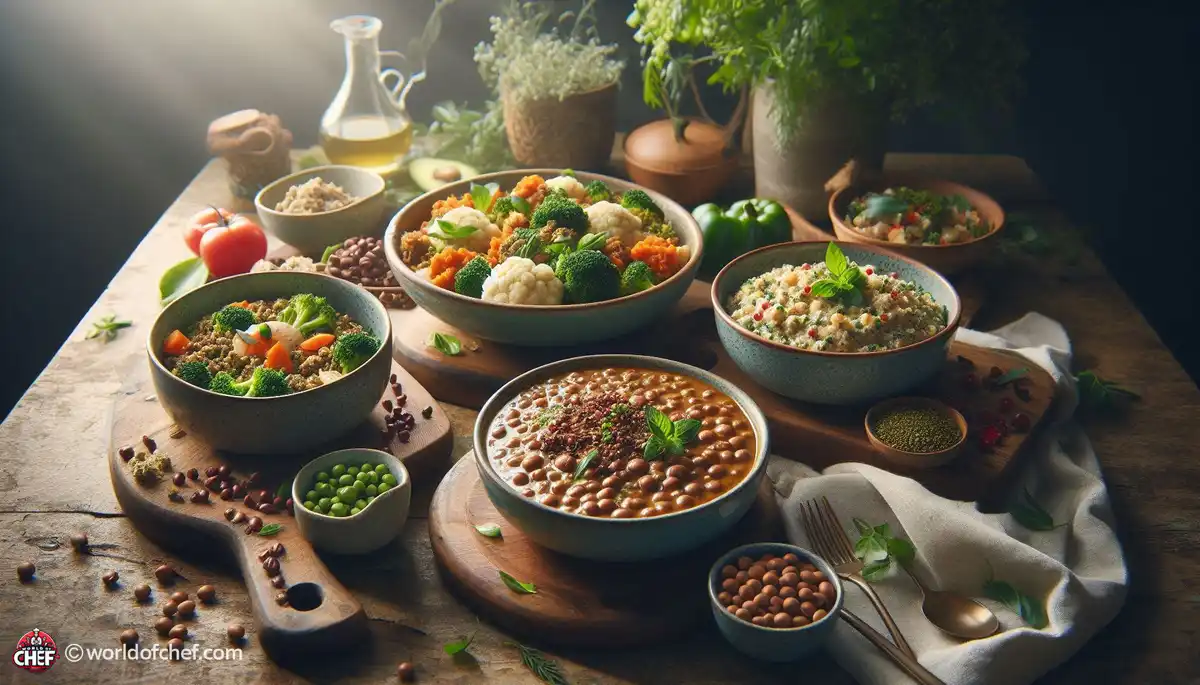

Dinner Delights: High-Fiber Recipes for Every Palate
Clarence Guido - Oct 7, 2024 - 7 min read


Fiber, often referred to as roughage or bulk, is the carbohydrate found in plant foods. Unlike other carbohydrates, fiber cannot be broken down into sugar molecules in your body. Instead, it passes relatively intact through your stomach, small intestine, and colon, helping you move waste and keeping you healthy.
There are two primary forms of fiber: soluble and insoluble. Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a sort of gel in the intestine that helps regulate blood sugar level and cholesterol. Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and adds bulk to the stool, thus enabling regularity and preventing constipation. Most plant foods contain some combination of both types of fiber, bringing varied Health Benefits.
Sufficient consumption of fiber in diet is crucial for optimal healthy benefits. Fibers improve easy digestion but carry their rich health benefit to include weight loss, protection on cardiovascular levels, and overall prevention of diseases. On the importance of the advantages of fiber, such immense importance means getting an ever healthier body overall when an individual learns how to include foods best on their list.
It enhances the body's ability to maintain a healthy digestive system. The soluble fiber holds water in it and transforms into a gel-like structure, thus softening the stool to be easily passed. On the other hand, the insoluble fiber increases the bulk in the stool; hence it hastens the transit time in the gut and decreases the risk of constipation. Fiber decreases the tendency of several digestive disorders including hemorrhoids, diverticulosis, and irritable bowel syndrome. Since fiber keeps people full, it is also vital in weight management.
Highly digestible foods tend to make people feel unsatisfied for a shorter time than low-digesting ones. Thus, one remains satisfied for a more extended period and tends to be less likely to overfeed. In addition, high-fiber foods have a lower calorie content and high nutrient content. Thus, they are suitable for those who would not like to gain excess body weight. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes into your diet will help you in the proper management of body weight and avoid unwanted gains in body weight.
Another important benefit of fiber is that it supports heart health. Soluble fiber lowers LDL cholesterol levels, or "bad" cholesterol, because it combines with cholesterol particles and excretes them from the body. With lower levels of LDL cholesterol, there will be less plaque building in the arteries, hence lower risk of heart disease and stroke. In addition, high fiber foods are usually rich in antioxidants and other heart-healthy nutrients that add support to cardiovascular health.
A variety of fiber-rich foods are believed to be needed to reap the benefits from them. Fiber can be easily incorporated into your diet by including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. In your diet, you should aim at introducing a variety of high fiber foods so that all you get is the required variation of nutrients and their benefit.
Try reading food labels when you go grocery shopping so you can easily detect high-fiber food products. You will be able to avoid certain products if you look for labeling like "high fiber," "good source of fiber," or "rich in fiber." In addition, read the ingredients list and look for fiber-rich whole grains, fruits, and vegetables instead of refined grains and processed food.
Increase the amount of fiber in your diet gradually if you are not used to taking large amounts of it because its sudden intake may cause some digestive discomfort, including bloating, gas, and cramping. Introduce small amounts of high-fiber foods into your diet and gradually increase the amount over time. You must also drink plenty of water throughout the day since fiber absorbs water and can lead to dehydration if not accompanied by enough fluids.
Although high-Fiber Intake has lots of health benefits, an increase in fiber should still not be excessive. Very much fiber, especially an upward spike in your level quickly, can lead to an assortment of digestive upsets including bloating and distension, gas and diarreah. This excessive fiber intake would additionally lead to the deprivation of certain minerals like calcium, iron, zinc, magnesium on a long-term scale while being absorbed. To avoid all these problems, take a balanced diet with several fiber-rich foods in the right quantities.
The need to appreciate is that various people have different requirements and tolerances for fiber. Some may require a lot of fiber than others based on age, gender, activity level, and their general health status. In addition, some health conditions, for example, gastrointestinal disorders or food intolerances, would need a change in the quantity of fiber you take. Seek a healthcare provider or a licensed dietitian to determine your specific needs and design a personalized diet to support those needs.
In conclusion, fiber is an important nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining optimal health. Promotes healthy digestion, helps in management of weight, improves heart health, and reduces the risk of chronic diseases. Benefits from fiber are undeniable. Know how important fiber is, incorporate fiber-rich foods in your diet, and live a healthier and more vibrant life. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds in your diet and snacks so that you could get enough daily fiber. Your body will appreciate that!

Clarence Guido - Oct 7, 2024 - 7 min read
Lydia Timmerman - Oct 6, 2024 - 6 min read

Logan Trowbridge - Oct 6, 2024 - 7 min read

Wayne Tobar - Oct 4, 2024 - 8 min read